Verification of 1D cell stationary advection diffusion schemes.
Verification of 1D cell stationary advection diffusion schemes.
This test case assesses the spatial convergence of the 1D stationary advection-diffusion equation with Dirichlet boundary conditions on left and right boundaries.
This case aims to:
The domain is the unit square in \([0,1]^2\).
We solve the stationary advection-diffusion equation:
\[ - \nu \Delta T + \mathbf{u} \cdot \nabla T = f \]
with null right-hand-side (i.e. \( f = 0 \)). The velocity is 1D and constant, \( \mathbf{u} = (u_x, 0) \), and the diffusion coefficient \( \nu = u_x/\mathrm{Pe} \), where the Péclet number is defined as:
\[ \mathrm{Pe} = \frac{u_x L}{\nu}. \]
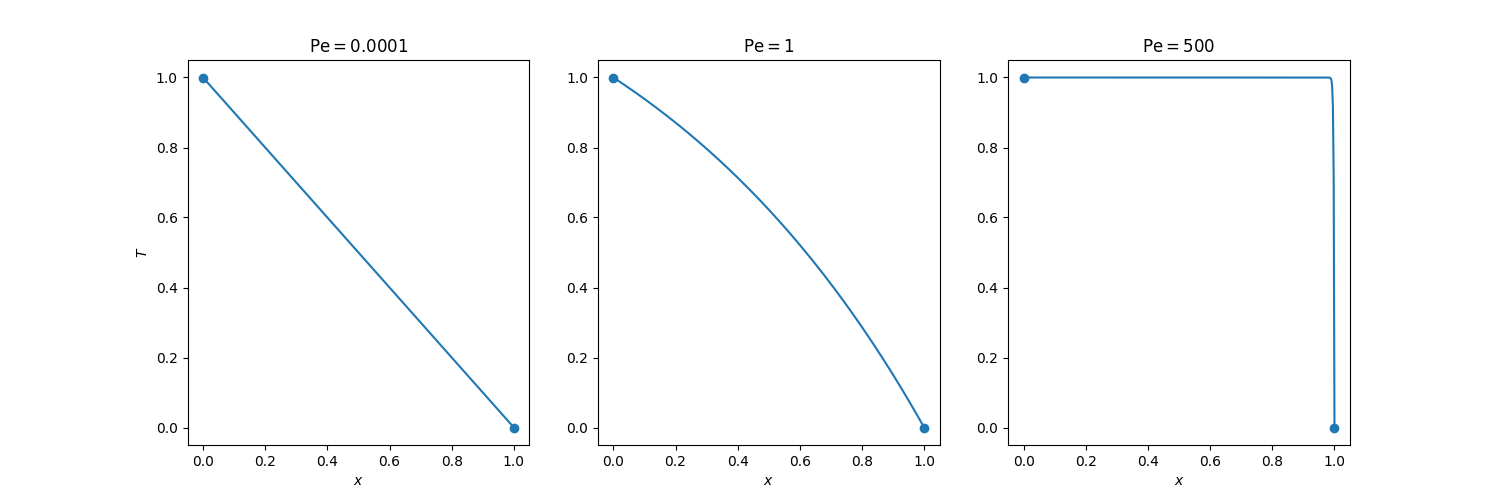
Since the problem is 1D in the x-direction, we expect the solution to be invariant in y.
Given Dirichlet boundary conditions on left and right, the associated exact solution is:
\[ \frac{T(x)-T_{\mathrm{left}}}{T_{\mathrm{right}} - T_{\mathrm{left}}} = \frac{e^{\frac{x \mathrm{Pe}}{L}} -1 }{e^{\mathrm{Pe}} -1}. \]
We define the mesh Péclet number:
\[ \mathrm{Pe}_h = \frac{u_x h}{\nu} \]
which reduces as the mesh is refined. That number is important for the study of the numerical solution's accuracy and stability.
| Boundary | Condition | Value |
|---|---|---|
| left | Dirichlet | \( T = 1 \) |
| right | Dirichlet | \( T = 0 \) |
| top & bottom | Neumann or Periodic | homogeneous ( \( \partial_y T = 0 \)) |
enable_temporal_term false).diffusion_scheme implicit o2_centered) or fourth (diffusion_scheme implicit o4_centered) spatial order with a star stencil.boundary_condition_scheme quadratic or boundary_condition_scheme cubic.The test cases can be run with the file test_cases/verification/cell_advection_diffusion_schemes/1d/energy/adv_diff_stationary.nts.
This graph confirms second, third and fourth-order convergence for different combinaisons of schemes, given a fourth-order cubic boundary condition scheme.
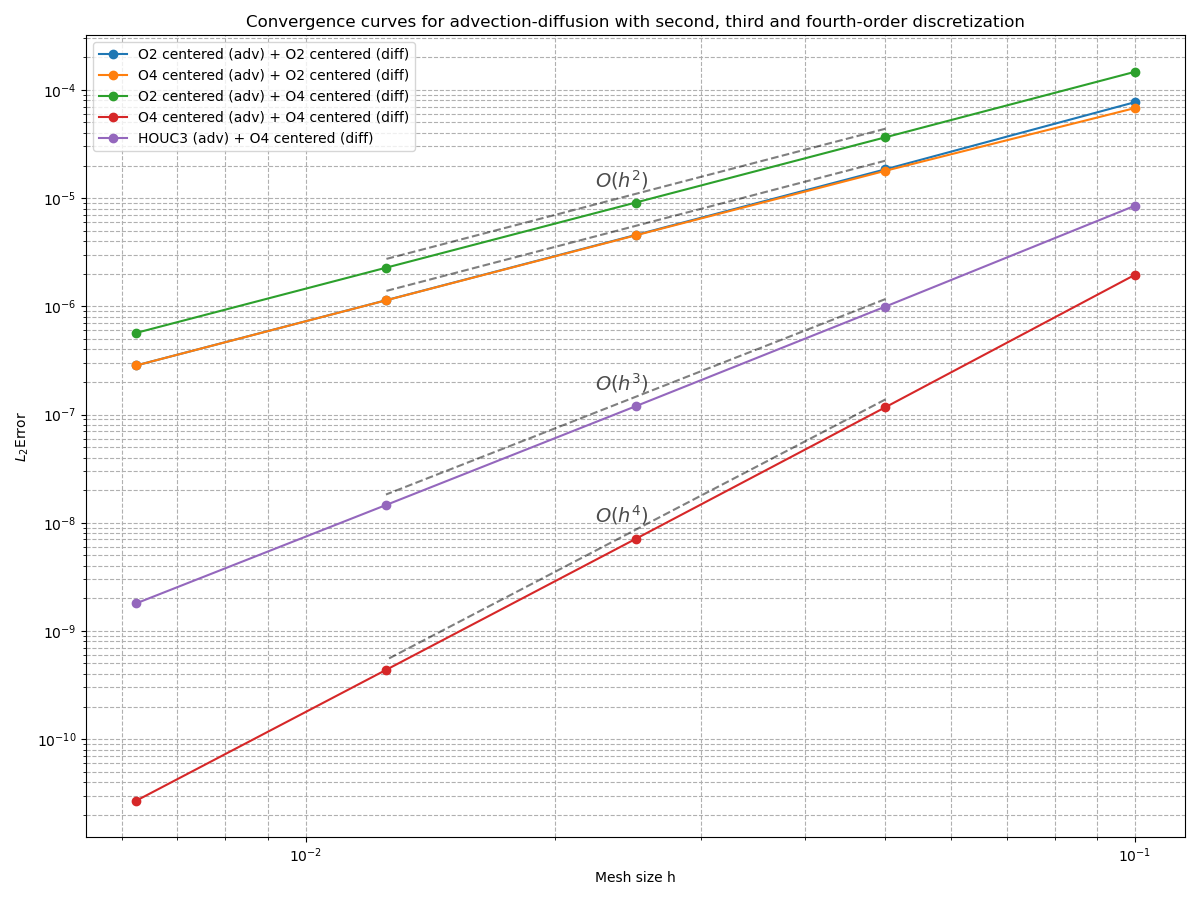
Note: Expected convergence orders are generally observed when the Péclet number is within the range \( 10^{-2} \leq \mathrm{Pe} \leq 10^{1} \).
In this test, we solve the steady advection-diffusion equation with very high diffusion, i.e. \( \mathrm{Pe} = 10^{-4} \). For that case, the exact solution is very smooth and nearly affine.
| Mesh | Temperature \( L_1 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_2 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_{\infty} \) error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×10 | 3.076298937809696e-13 | n/a | 3.992327850393273e-13 | n/a | 8.648082250317657e-13 | n/a |
| 20×20 | 4.0958402468260767e-13 | -0.413 | 4.894999418797806e-13 | -0.294 | 9.443557047461582e-13 | -0.127 |
| 40×40 | 3.31803614531806e-13 | 0.304 | 4.057242171008019e-13 | 0.271 | 9.171552406428418e-13 | 0.042 |
| 80×80 | 3.583580905164393e-13 | -0.111 | 4.2951250006921456e-13 | -0.082 | 9.712022852603752e-13 | -0.083 |
| 160×160 | 3.0775601287023584e-13 | 0.220 | 3.9487576338533454e-13 | 0.121 | 1.1652900866465643e-12 | -0.263 |
| Mesh | Temperature \( L_1 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_2 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_{\infty} \) error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×10 | 3.0441878184905843e-13 | n/a | 3.97507249654718e-13 | n/a | 8.701928067011977e-13 | n/a |
| 20×20 | 4.115876996863e-13 | -0.435 | 4.921520868821791e-13 | -0.308 | 9.541256673628595e-13 | -0.133 |
| 40×40 | 3.344625206132267e-13 | 0.299 | 4.103052387958695e-13 | 0.262 | 9.10715947100016e-13 | 0.067 |
| 80×80 | 3.474891129505962e-13 | -0.055 | 4.1671838393714256e-13 | -0.022 | 9.700747150009903e-13 | -0.091 |
| 160×160 | 2.8254159467716893e-13 | 0.299 | 3.6662711714813503e-13 | 0.185 | 9.992145999504487e-13 | -0.043 |
No meaningful convergence can be deduced. The numerical solution reaches a plateau due to limited machine precision.
The solution is practically a straight line — fitting it with a 4th-order polynomial yields negligible residuals.
In this section, we investigate the numerical behavior of the advection–diffusion equation for a high Péclet number (Pe = 500), where the advection term dominates. The solution is quite sharp, because of superior advection, and challenges the numerical schemes.
Diffusion is discretized using a 4th-order centered scheme, while boundary conditions are handled with a cubic scheme. Only the advection scheme is varied in order to compare accuracy and possible oscillations.
The tables in the appendix show convergence rates associated to the the advection scheme (from 1 to 4), as expected. Be careful that, at Péclet number larger than 2, oscillations may alter the convergence rate. We thus chose to start the mesh convergence at \( \mathrm{Pe} = 3.125 \).
The min/max conservation of the solution is, ideally, expected. Depending on the scheme, we observe oscillations (near the right boundary) due to the numerical properties of the advection-diffusion coupling, depending on the mesh Péclet number. Oscillations can be proven to appear for \(\mathrm{Pe}_h \ge 2\) with the second-order centered schemes and can be tackled with the use of an upwind advection scheme, as for example with the first order scheme. Moreover, boundary schemes have influence as they are coupled with the advection-diffusion schemes. Figure 3 illustrates the min/max values for every couple of schemes.
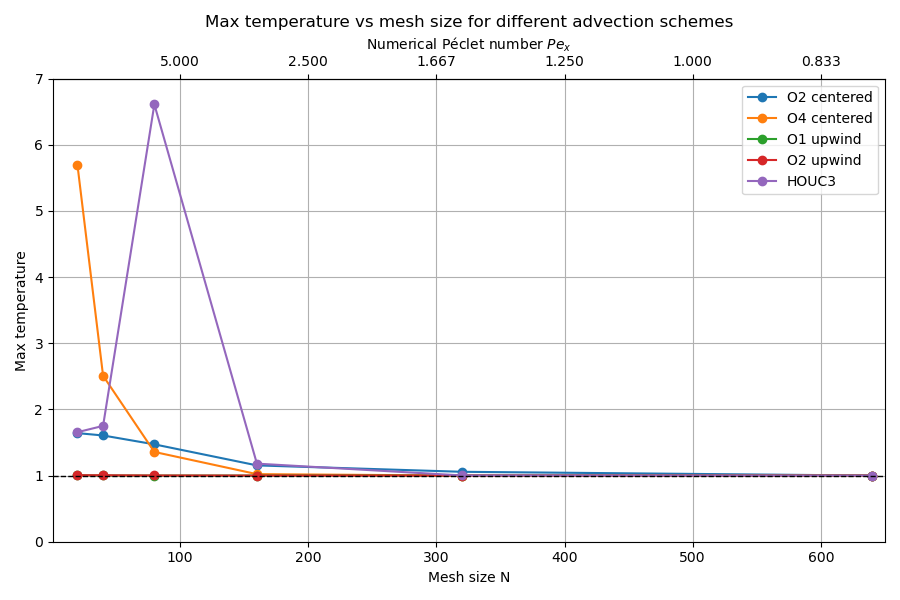
The convergence study of the maximum and minimum values for various advection schemes shows the following trends:
In summary, low-order upwind schemes provide stability but at the cost of accuracy, whereas higher-order centered schemes achieve better convergence but are highly sensitive to the mesh size and the numerical Péclet number.
Centered schemes show important oscillations in this regime. A more stable upwind scheme should be preferred when \(\mathrm{Pe}_h \gg 2\).
| Mesh | Temperature \( L_1 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_2 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_{\infty} \) error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×10 | 7.110313317222103e-05 | n/a | 7.709319716524254e-05 | n/a | 1.049915200799223e-04 | n/a |
| 20×20 | 1.6841227668907578e-05 | 2.078 | 1.8455978215433737e-05 | 2.063 | 2.5470315403008925e-05 | 2.043 |
| 40×40 | 4.151369355808782e-06 | 2.020 | 4.562944018403443e-06 | 2.016 | 6.311104322143102e-06 | 2.013 |
| 80×80 | 1.034136265615827e-06 | 2.005 | 1.1375325758807836e-06 | 2.004 | 1.5743330975537262e-06 | 2.003 |
| 160×160 | 2.5830174347907765e-07 | 2.001 | 2.8418239883512675e-07 | 2.001 | 3.933474835848827e-07 | 2.001 |
| Mesh | Temperature \( L_1 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_2 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_{\infty} \) error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×10 | 6.1297299113537e-05 | n/a | 6.801444014405986e-05 | n/a | 9.512071508899211e-05 | n/a |
| 20×20 | 1.6223701542502303e-05 | 1.918 | 1.788546553923447e-05 | 1.927 | 2.4833514004063417e-05 | 1.937 |
| 40×40 | 4.112602358413217e-06 | 1.980 | 4.527143592391392e-06 | 1.982 | 6.270596994872868e-06 | 1.986 |
| 80×80 | 1.0317074436703357e-06 | 1.995 | 1.1352895867341748e-06 | 1.996 | 1.5718092443162135e-06 | 1.996 |
| 160×160 | 2.5814952917317504e-07 | 1.999 | 2.840417874558925e-07 | 1.999 | 3.9318873235050233e-07 | 1.999 |
| Mesh | Temperature \( L_1 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_2 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_{\infty} \) error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×10 | 1.3467017749612927e-04 | n/a | 1.4710428667780387e-04 | n/a | 2.0241173992319172e-04 | n/a |
| 20×20 | 3.320520595429137e-05 | 2.020 | 3.6470054569953545e-05 | 2.012 | 5.045437517980922e-05 | 2.004 |
| 40×40 | 8.27268254514762e-06 | 2.005 | 9.09823485012667e-06 | 2.003 | 1.2591330352362817e-05 | 2.003 |
| 80×80 | 2.0663862222483234e-06 | 2.001 | 2.273334533247571e-06 | 2.001 | 3.146745152227126e-06 | 2.000 |
| 160×160 | 5.164850566319967e-07 | 2.000 | 5.682562402794638e-07 | 2.000 | 7.865738679280199e-07 | 2.000 |
| Mesh | Temperature \( L_1 \) error | order | Temperature \( L_2 \)error | order | Temperature \( L_{\infty} \) error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×10 | 1.8283083294221013e-06 | n/a | 1.9581343939158866e-06 | n/a | 3.633710309910998e-06 | n/a |
| 20×20 | 1.0946009252247798e-07 | 4.062 | 1.1670760024008423e-07 | 4.069 | 2.3877613297002e-07 | 3.928 |
| 40×40 | 6.6902440714754375e-09 | 4.032 | 7.0867924923823664e-09 | 4.042 | 1.5314548611894407e-08 | 3.963 |
| 80×80 | 4.133900781313605e-10 | 4.016 | 4.35838628830309e-10 | 4.023 | 9.698106467198597e-10 | 3.981 |
| 160×160 | 2.564579322882323e-11 | 4.011 | 2.697445263744445e-11 | 4.014 | 6.10157957145474e-11 | 3.990 |
| N | Pe = 500/N | Max temperature | order | Temperature L1 error | order | Temperature L2 error | order | Temperature Linf error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160×4 | 3.125 | 1.153764989873273 | n/a | 0.032740481289562244 | n/a | 0.39693025446553204 | n/a | 5.018211188769706 | n/a |
| 320×8 | 1.5625 | 1.0569369335830208 | n/a | 0.0014606197102087213 | 4.486 | 0.016879794190739393 | 4.556 | 0.24988288858223895 | 4.328 |
| 640×16 | 0.7813 | 1.0000000000001505 | 0.766 | 0.00024063105670532294 | 2.602 | 0.002692066861112279 | 2.649 | 0.04371007887532541 | 2.515 |
| 1280×32 | 0.3906 | 0.999999999999995 | 38.413 | 5.339634677626918e-05 | 2.172 | 0.0005965366762243941 | 2.174 | 0.00984772635872444 | 2.150 |
| 2560×64 | 0.1953 | 0.9999999999999953 | nan | 1.2887116115095763e-05 | 2.051 | 0.00014405486720236158 | 2.050 | 0.0023667574359877985 | 2.057 |
| 5120×128 | 0.09765 | 0.9999999999999923 | nan | 3.190197134465769e-06 | 2.014 | 3.5666225899604904e-05 | 2.014 | 0.0005868121054873887 | 2.012 |
| N | Pe = 500/N | Max temperature | order | Temperature L1 error | order | Temperature L2 error | order | Temperature Linf error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160×4 | 3.125 | 1.0215671867893708 | n/a | 0.0021579702242837625 | n/a | 0.017135833479726734 | n/a | 0.16077199660757047 | n/a |
| 320×8 | 1.5625 | 1.0000000000000209 | n/a | 0.0001833965602015934 | 3.557 | 0.0019305815968240065 | 3.150 | 0.02815433401854961 | 2.514 |
| 640×16 | 0.7813 | 1.00000000000019 | nan | 1.2656857257610122e-05 | 3.857 | 0.00016530245969005461 | 3.546 | 0.003733454536263281 | 2.915 |
| 1280×32 | 0.3906 | 0.9999999999999953 | nan | 7.995941841933956e-07 | 3.985 | 1.1551299562067275e-05 | 3.839 | 0.0003625962949609096 | 3.364 |
| 2560×64 | 0.1953 | 0.9999999999999953 | nan | 4.852058923825658e-08 | 4.043 | 7.188203201799841e-07 | 4.006 | 2.8785365959432818e-05 | 3.655 |
| 5120×128 | 0.09765 | 0.9999999999999927 | nan | 2.9636024146894595e-09 | 4.033 | 4.295639857669098e-08 | 4.065 | 2.0373293133507664e-06 | 3.821 |
| N | Pe = 500/N | Max temperature | order | Temperature L1 error | order | Temperature L2 error | order | Temperature Linf error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160×4 | 3.125 | 1.000000000000024 | n/a | 0.00178407958547918 | n/a | 0.015611966454890555 | n/a | 0.17699202627548793 | n/a |
| 320×8 | 1.5625 | 1.0000000000000393 | n/a | 0.0011144526700285226 | 0.679 | 0.010590010479147571 | 0.560 | 0.12694170297612772 | 0.480 |
| 640×16 | 0.7813 | 1.0000000000002187 | -3.550 | 0.0006421739058642161 | 0.795 | 0.006556698384443601 | 0.692 | 0.10025786391570257 | 0.340 |
| 1280×32 | 0.3906 | 0.9999999999999952 | nan | 0.0003500898079776607 | 0.875 | 0.003734129018085411 | 0.812 | 0.05858256434996889 | 0.775 |
| 2560×64 | 0.1953 | 0.9999999999999947 | 8.653 | 0.00018411528695549324 | 0.927 | 0.002009794417375664 | 0.894 | 0.03232944085819922 | 0.858 |
| 5120×128 | 0.09765 | 0.9999999999999941 | -0.000 | 9.468619749833585e-05 | 0.959 | 0.0010459173378449525 | 0.942 | 0.017008866182353866 | 0.927 |
| N | Pe = 500/N | Max temperature | order | Temperature L1 error | order | Temperature L2 error | order | Temperature Linf error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160×4 | 3.125 | 1.0000032957168814 | n/a | 0.0009178047177706905 | n/a | 0.008561817070250147 | n/a | 0.10011305907094714 | n/a |
| 320×8 | 1.5625 | 1.0000000000000253 | n/a | 0.0004995970894534595 | 0.877 | 0.0050073749466989495 | 0.774 | 0.060430663902330206 | 0.728 |
| 640×16 | 0.7813 | 1.0000000000002325 | nan | 0.0002142985298368106 | 1.221 | 0.002290881862251645 | 1.128 | 0.03683366807404387 | 0.714 |
| 1280×32 | 0.3906 | 0.9999999999999919 | nan | 7.373808539021602e-05 | 1.539 | 0.0008125205277880098 | 1.495 | 0.013232087355502187 | 1.477 |
| 2560×64 | 0.1953 | 0.9999999999999931 | nan | 2.1747303890842297e-05 | 1.762 | 0.00024213227991520732 | 1.747 | 0.003965313163662443 | 1.739 |
| 5120×128 | 0.09765 | 0.9999999999999918 | nan | 5.891604471912937e-06 | 1.884 | 6.57966525788961e-05 | 1.880 | 0.0010814264548021368 | 1.874 |
| N | Pe = 500/N | Max temperature | order | Temperature L1 error | order | Temperature L2 error | order | Temperature Linf error | order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160×4 | 3.125 | 1.1802836813843247 | n/a | 0.0038358234052973477 | n/a | 0.039640885324899636 | n/a | 0.4861195619445483 | n/a |
| 320×8 | 1.5625 | 1.0016855083081044 | n/a | 0.0005094592900704622 | 2.912 | 0.005462929672300457 | 2.859 | 0.07667184179685149 | 2.665 |
| 640×16 | 0.7813 | 1.0000000000001312 | 6.727 | 7.122433546815692e-05 | 2.839 | 0.0007795536076492235 | 2.809 | 0.012011844350684475 | 2.674 |
| 1280×32 | 0.3906 | 0.999999999999994 | 33.516 | 9.500482137198837e-06 | 2.906 | 0.00010531033467621856 | 2.888 | 0.0017097491033888357 | 2.813 |
| 2560×64 | 0.1953 | 0.9999999999999951 | nan | 1.220801894038357e-06 | 2.960 | 1.3609706676876384e-05 | 2.952 | 0.00022249583055145017 | 2.942 |
| 5120×128 | 0.09765 | 0.9999999999999921 | nan | 1.5420170009300998e-07 | 2.985 | 1.7224268147333265e-06 | 2.982 | 2.8305948745921405e-05 | 2.975 |