The following guidelines describes how project files are organized.
The usage of each sub-directory is listed below:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
doc | Doxygen generated documentation |
logo | The Notus logo |
src | Fortran source files |
std | Standard database |
test_cases | Test case description files |
tools | Useful development and validation scripts |
src directoryThe sources of Notus are devided into 4 parts:
libnotus.a. Corresponding files are in src/lib.libnotus.a. They can be found in src/notus.src/doc.src/unit_testing directory.The library architecture is based on 8 different modules that the developer will find in the corresponding source directories. The following section describes each module as well as its interaction with others.
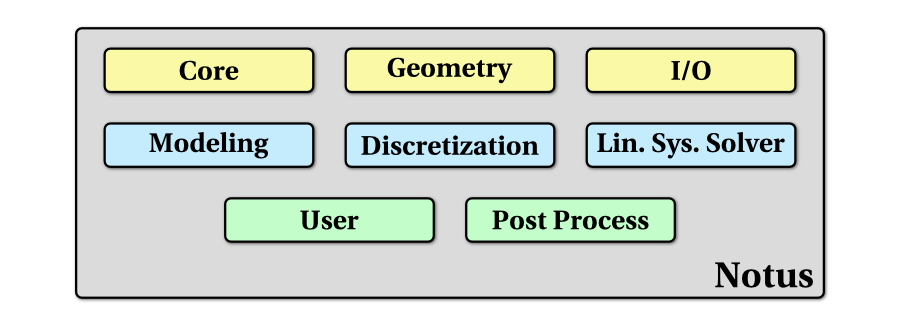
src/lib directoryThe User module is the place where the advanced user can develop its own code when the NTS files aren't sufficient for his/her needs.
The Core module furnishes the base code on which is built the library. It contains the following sub-modules:
The Modeling module is the place where the equations of the physical models (see Brief description of models and equations) are solved. To do so, it uses principally the Discretization and the Linear System Solver modules. This is where the model developer will integrate his own code. We use high-level numerical methods term for this module.
The following sub-modules are furnished in the library and can serve as examples:
The Discretization module furnishes all the computation procedures and functions that are (mainly) used by the Modeling module to effectively solve the equations. For example, the developer will find there all the differential cell or face operator implicit discretization routines, the explicit differential operators (gradient, divergence, etc.) and finite difference schemes. We use the low-level numerical methods term for this module. The model developer will use this part of the library, whereas the numerical developer will develop his own methods inside it.
It is divided in sub-modules:
The Post process module furnishes all the tools that are used and can be used to extract numerical and physical diagnostics from the computed data. For example, one can use this module to compute the \(L_2\) norm of the error to a reference solution, or the strain rate based on the velocity field.
It is divided in sub-modules:
The Geometry module contains procedures related to the discrete and physical geometry of the problem. It is separated in two distinct sub-modules:
The Linear system solver module handles the different solvers encapsulated into Notus and the external solver interfaces. It furnishes the procedure to use the three following solvers:
The Input/Output module proposed the various procedures to read the input data and write output information and results. It contains also the log and debug procedures to display/save various information during the calculus.
It is divided in sub-modules:
notus_log function for printing specific output during the calculationsFor a complete view of this directory at a lower level, see Modules and topics on left menu. It contains numerical method and source descriptions.
src/notus directoryThe main program notus.f90 is found in src/notus directory. It is described next section (Code overview).
Routine finalize_initialization.f90 finalizes the initialization process of a simulation. It is called just before the time loop.
test_cases subdirectoryFortran programs relative to some test cases that cannot be completely described by the User Interface are present in the test_cases subdirectory. For instance, it may be some time dependant velocity field, spatial dependant boundary conditions, etc. There is one subdirectory associated to the each test case that need such routines. In this case, a keyword is present in the corresponding NTS file. For instance:
test_case tc_vof_sheared;
These routines may be called to initialize, prepare next time loop iteration, or for post-processing purposes.
ui subdirectoryThe user interface is in the ui sub-directory.
comand_line subdirectoryIt contains routines that read Notus command line.
src/doc directoryThis directory contains doc sources (Markdown .md files) which are not directly linked to a source file but describe some basic concepts of the code (build, source organization, description of the domain, etc.).
src/unit_testing directoryThis directory contains the Unit Testing ('UT') subdirectories that are aimed to test and validate each individual element/part of the code, separately.
test_cases directoryThis directory contains the test cases NTS files that are used to verify and validate Notus. Verification analyzes the solution of the code when an exact solution of the problem exists (or is eventually manufactured). It is essentially a mathematical process. Validation checks the capacity of the code to represent a physical problem (flow, heat transfer, etc.) that do not have an exact solution.
Thus, the Notus test cases are divided into 2 groups, verification and validation test cases. Each test case is described by an NTS file that is read by the parser of Notus. It follows a specific succession of information (grammar) about the domain and the mesh, the modeling and the numerical methods, and finally about post-processing.
The description of each test case and their expected results can be found in these two pages verification and validation.
Enventually, some specific routines associated to initialization, time dependant source terms or boundary conditions, etc., are defined in src/notus/test_cases directory, that follows the same tree then then the test_cases directory.
std directoryThis directory contains the standard Notus database that is reduced at present time to the fluid physical properties database physical_properties.nts.